Understanding Fixed and Variable Expenses in Budgeting
Budgeting is one of the most important steps in managing your money. It helps you know where your money goes, keeps your spending under control, and brings you closer to your financial goals. But before you create a good budget, you need to understand the two main types of expenses: fixed expenses and Variable Expenses
In this post, we’ll explain what these two types of expenses are, give examples, and show how they affect your budget in both good and bad ways. Let’s get started!
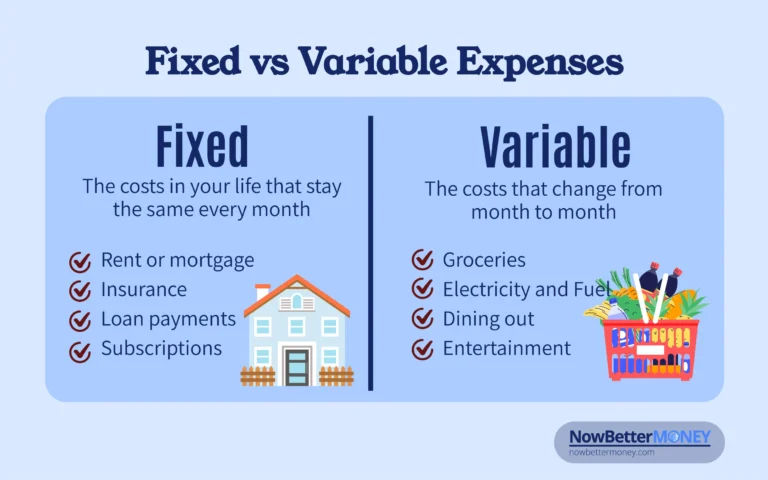
What Are Fixed Expenses?
Fixed expenses are the costs in your life that stay the same every month. These are usually things you must pay, no matter what. They don’t change based on how much you use something or what your habits are.
Examples of Fixed Expenses:
Why Fixed Expenses Are Important
Fixed expenses are easy to plan for because you know how much they’ll cost every month. They help you build the base of your budget. When you know how much of your income goes to fixed costs, it’s easier to plan what’s left for other spending or saving.
But there’s also a downside. Since you have to pay them no matter what, fixed expenses can be hard to change if your income drops. For example, if you lose your job, you still need to pay your rent or loan payments.
What Are Variable Expenses?
Variable expenses are the costs that change from month to month. These expenses depend on how much you use or how you choose to live. Some months they can be low, other months they can be high.
Examples of Variable Expenses:
Why Variable Expenses Are Important
Variable expenses give you flexibility. You can usually control how much you spend on these. If you’re trying to save money, you can cut back on eating out or entertainment.
However, because they change, variable expenses are harder to predict. Without tracking them carefully, they can cause you to spend more than you plan.
Positive and Negative Effects on Budgeting
Now that you know the difference between fixed and variable expenses, let’s see how they affect your budget. Each type has both positive and negative effects, depending on your income, habits, and how well you plan.
Here’s a simple table to help you understand:
|
Type of Expense |
Positive Effects |
Negative Effects |
|---|---|---|
|
Fixed Expenses |
. Easy to plan for . Predictable each month |
. Hard to reduce quickly . Takes up a big part of income |
|
Variable Expenses |
. Flexible . Easy to cut when needed |
. Hard to predict . Can cause overspending if not tracked |
Explanation:
Balancing Fixed and Variable Expenses in Your Budget
The best way to manage your money is to balance your fixed and variable expenses. Here are some tips to help you:
1. Know Your Numbers
Start by writing down all your fixed and variable expenses. Look at your last 2–3 months of spending. Use bank statements, receipts, or a budgeting app.
Create two lists:
2. Calculate Percentages
Try to see what percentage of your income goes to fixed vs variable costs. A good rule is:
If your fixed expenses are more than 60%, you might feel tight with your money.
3. Set Limits for Variable Spending
Once you know your average variable spending, set a monthly limit. For example, decide to spend no more than $200 on groceries or $100 on entertainment. Track it every week to stay on target.
4. Reduce Unnecessary Fixed Costs
Some fixed expenses can be reduced:
Even small changes can free up a lot of money in the long term.
5. Be Flexible and Adjust
Your budget is not fixed forever. Life changes — income goes up or down, new expenses come in. Review your budget monthly. Adjust fixed and variable costs based on your current goals and situation.
Conclusion
Understanding fixed and variable expenses is a big step toward becoming better with money. Fixed expenses are steady and easy to plan for, but they give less room to adjust. Variable expenses are flexible and can be reduced, but they need more attention and control.
By knowing the difference and learning how each type affects your budget, you can make smarter choices, save more money, and feel more confident every time you spend. Start today by listing your own expenses and see how balanced your budget really is.

NowBetterMONEY, where is a hub shares practical tips on budgeting, saving, and debt management. I uses a personal finance tracker to monitor spending and savings, helping readers take control of their finances and build long-term financial stability with simple, actionable strategies. Author Bio


